Relay
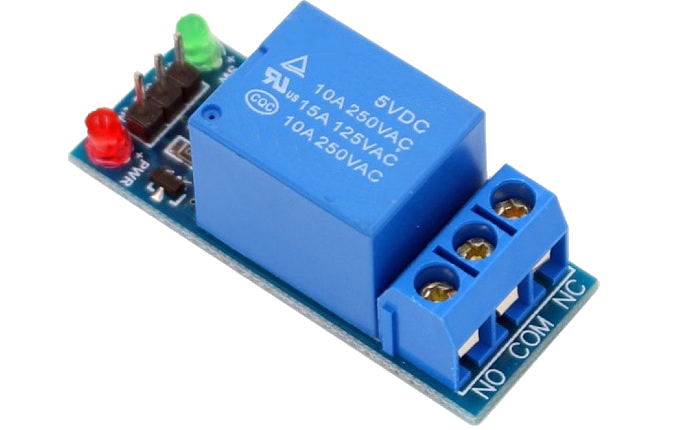
When working on projects that involve different components, managing powerful workloads can be challenging. For example, an electric motor or lighting lamps require high current and voltage levels that cannot be controlled directly by a controller, except for low-power LED lights. Direct control could lead to damaging the controller in case of short circuits or sudden power surges.
To solve this problem, relays are an excellent choice as they can control loads by closing the contact needed based on the commands from the controller. If the controller can operate with low voltages like 5 or 3.3 volts, the switched load can be much more powerful, up to 220V AC.
If you're dealing with an electric motor, it's better to use a separate motor controller. But if you only need to turn on the engine without adjusting the speed or soft start, you can use a relay. The simplest relay is an electro-mechanical relay with a reed switch. It mechanically closes the contact through which the main load applies under the influence of a logical signal. The advantage of such relays is that they're cheap and versatile. It doesn't matter whether direct or alternating current flows through it when the contact is mechanically closed. However, it has some disadvantages, such as clicking sounds when triggered and limitations in performance and service life due to mechanical parts. If you don't need to switch the load multiple times per second and don't require the relay to serve for years, this option is optimal.
If a mechanical relay is not suitable, solid-state relays can be used. Unlike mechanical relays, they have no moving parts and switching occurs using semiconductor components like thyristors or transistors. These relays are compact, silent, and have a long service life and switching speed. However, they're sensitive to overloads, even short-term excesses of the transmitted current and voltage, and have a small additional resistance in the closed state.
Several other specific types of relays, such as photovoltaic and induction relays, are available. But if the project requirements don't need them, you're unlikely to use them.
The choice of relay depends on the load that needs to be controlled and the level of the control signal. Electro-mechanical relays can be controlled by a 5V logic signal, so they can be connected directly to the controller outputs. More powerful relays can be controlled by a voltage of 12V and higher. In such cases, you may need to install an additional amplifying transistor or make a chain of several relays.
Relays are one of the easiest electrical circuit components to learn. They're essential in any practical application that manages real loads.
Wireless Motor Control System for turning security cameras, opening gates, blinds or solar panels
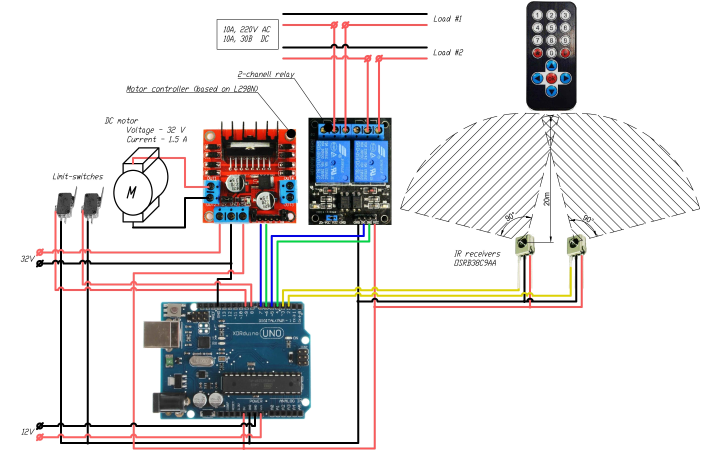
Using infrared receivers and a control panel, it provides remote control of electrical equipment functions. To ensure convenient control without the need to accurately point the remote control towards the control system, several infrared receivers are installed, with overlapping fields of view
Electrical load shedding system with temperature sensor
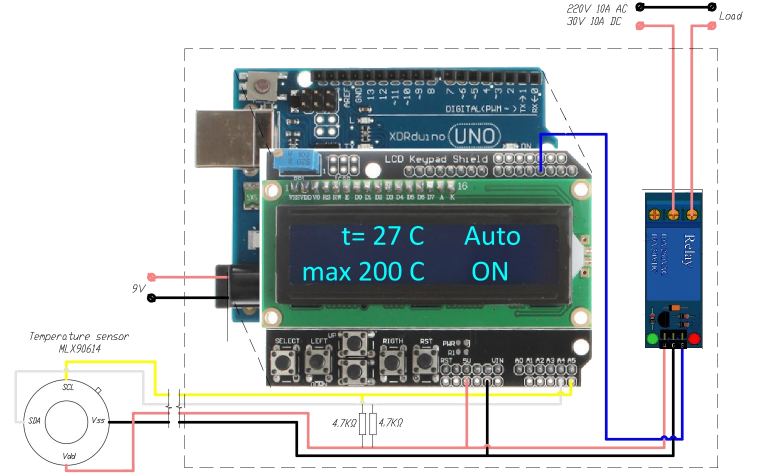
The system is designed for emergency shutdown of electrical load based on the readings of a wireless infrared temperature sensor
The MLX90614 infrared non-contact thermometer measures the temperature of an object and transmits the data to the controller, which turns on or off the relay that controls the load
Door Lock with face recognition by neural network
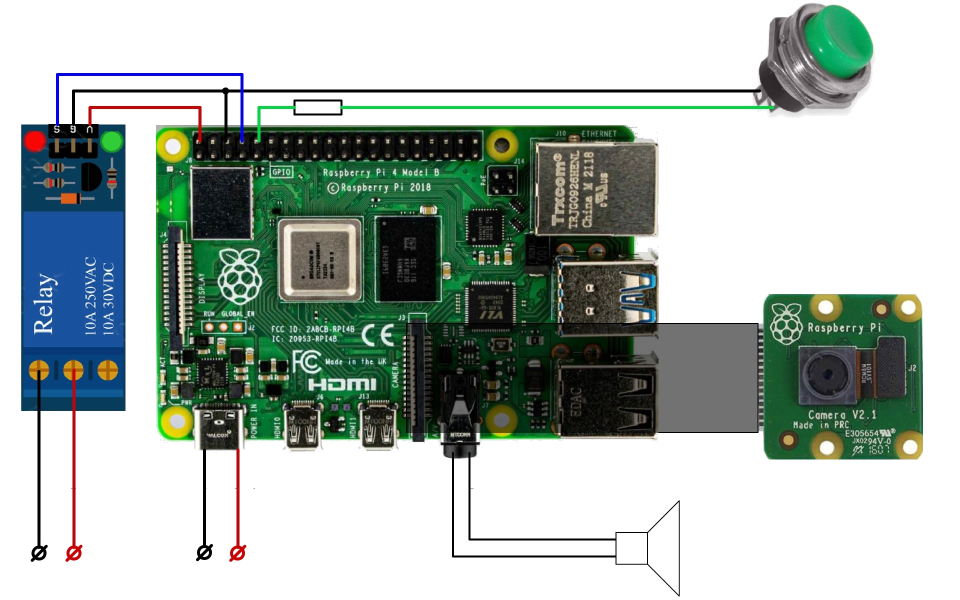
Door lock with unlocking based on facial recognition results (from the entrance camera). The door is closed with an electric lock, which can be opened using a relay. After pressing the button, a photo of the person standing in front of the door is taken by the camera and a short buzzer sounds. After this, the controller is compared with a reference face using a facial recognition system based on a neural network.
Briefcase with riddles to use in escape room amusement
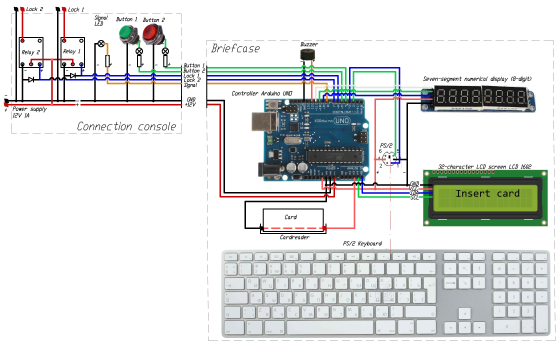
According to the plot of the game, the briefcase is part of the puzzle and must be used in a chain of tasks to open the exit door. The briefcase can be connected to a stationary connection console from which the door lock is unlocked. All actions are accompanied by messages on a numerical display, character LCD screen, and sound signals from a buzzer
Automated ballast discharge from a balloon
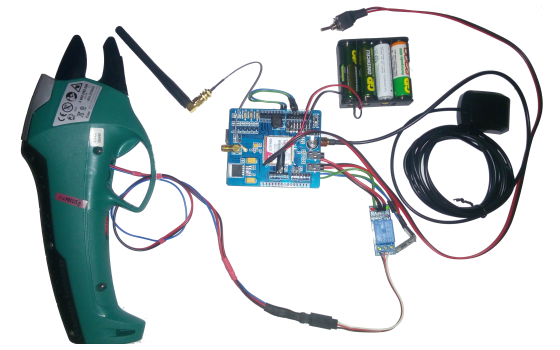
Automated ballast discharge from a balloon using GPS coordinates with a GSM communication channel. The system is installed on a balloon and is designed for emergency ballast release to avoid a collision with the ground in conditions when the balloon driver for some reason does not do this on his own
Stair lighting control system with traveling wave effect
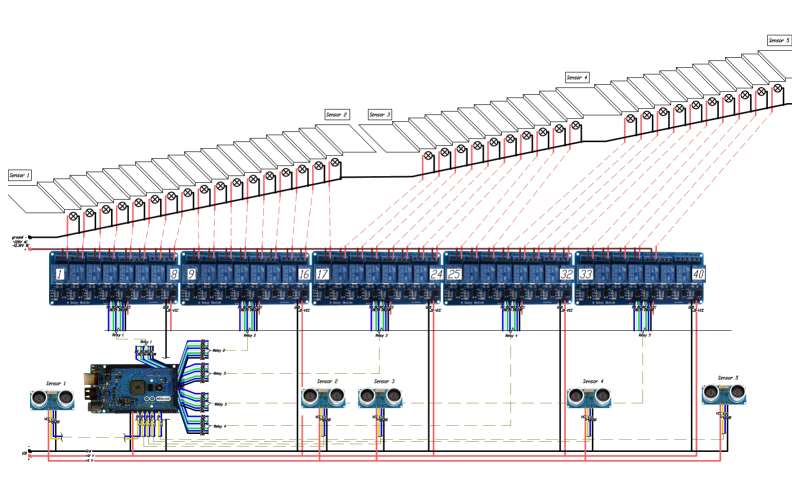
Individual staircase lighting control system with a traveling wave effect. Creates the effect of a traveling wave - alternately turning on the lighting of each step moving away from a walking person
Water pumping control system
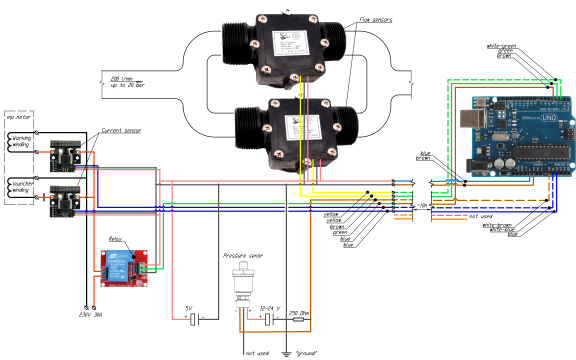
The system for installation on a pipeline for liquids pumping and control of the transportation process. Includes fluid flow sensors, motor current sensor and control relay for online control of process parameters, logging, emergency automatic and manual control of pumping.
Irrigation control system
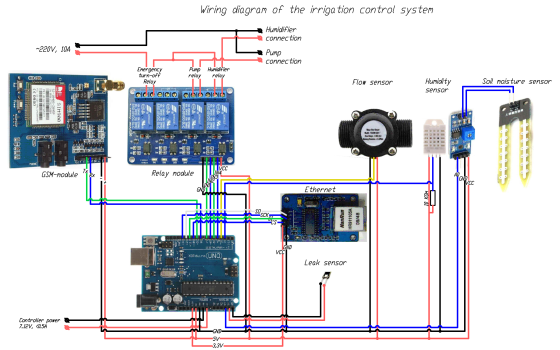
Irrigation control system for automatic maintenance of plant climate parameters using sensors, control via web interface and remote informing via mobile network
 Books
Books Technology
Technology Electronics
Electronics DC motors
DC motors Raspberry Pi Controllers
Raspberry Pi Controllers Relay
Relay Temperature sensors
Temperature sensors Analog sensors
Analog sensors Digital sensors
Digital sensors ADC
ADC Bluetooth
Bluetooth Radio communication 2.4 GHz
Radio communication 2.4 GHz LCD-screen
LCD-screen All tags
All tags Programming
Programming Weaponry
Weaponry Projects
Projects