Images

Images, in the form of photos, graphs, diagrams, or pictograms, simplify the user's interaction with the system. A quick glance at the panel with graphics can help users find the information they need without having to search through a text interface.
In 3D printing, loading an image of what you want to print is essential. Although the printer will process low-level commands for moving and printing, the average user may not know how to read G-codes. Having an image of what is being printed can help users understand what is happening and respond quickly to any errors that may occur.
Conventional microcontrollers, like the Arduino, are not ideal for working with full-fledged graphics. These controllers are capable of generating simple graphics, but their power and memory are not sufficient for storing full-fledged images. To work with images, additional peripherals are necessary, and the microcontroller will only generate commands for control.
However, minicomputers like the Raspberry Pi are well-suited for working with images. They have connectors for cameras and displays, enough memory and computing power to store and encode/decode photos, and a vast number of ready-made libraries for working with graphic files.
Full-fledged windowed applications take over all image processing functions. Using standard libraries, you can use complex algorithms to create or edit images. Modern computers have enough power to perform many actions almost instantly.
Ultraviolet 3D Printer with table swinging
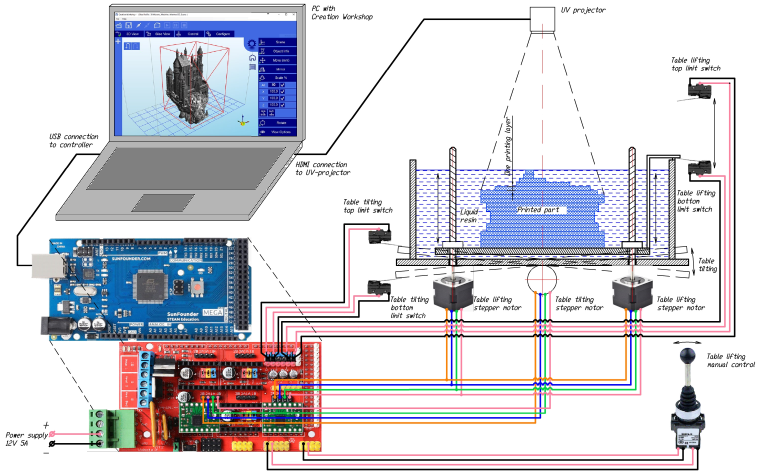
UV curing resin 3D printer with table rocking for better mixing and manual table lift control The part is printed from a liquid resin that hardens under the influence of ultraviolet light. Due to the fact that the thickness of the layers is quite small, after immersion the resin does not always reach the entire surface of the part. To avoid this, use the “Table Rocking” function in between exposures
Door Lock with face recognition by neural network
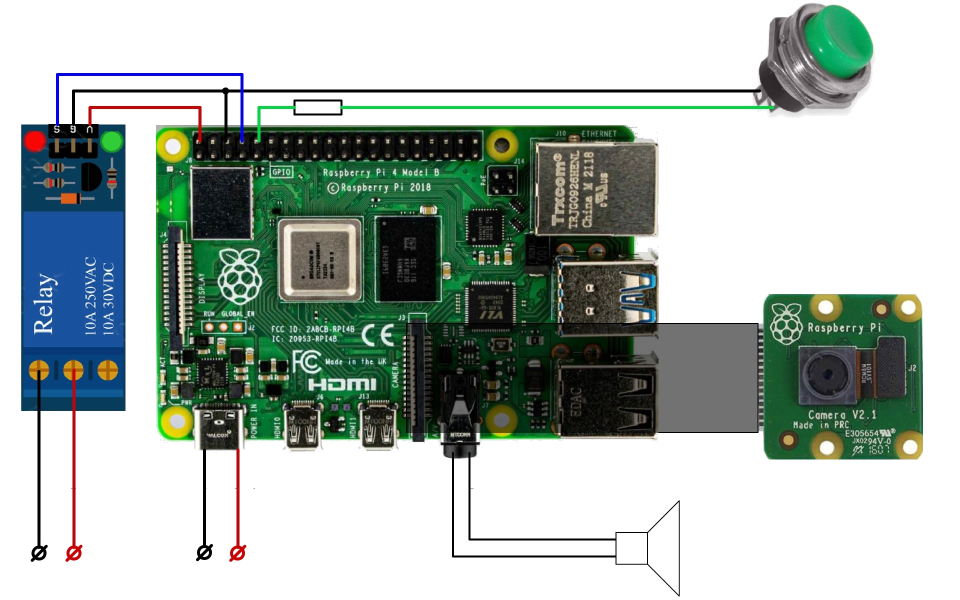
Door lock with unlocking based on facial recognition results (from the entrance camera). The door is closed with an electric lock, which can be opened using a relay. After pressing the button, a photo of the person standing in front of the door is taken by the camera and a short buzzer sounds. After this, the controller is compared with a reference face using a facial recognition system based on a neural network.
Smart glasses with blink detector
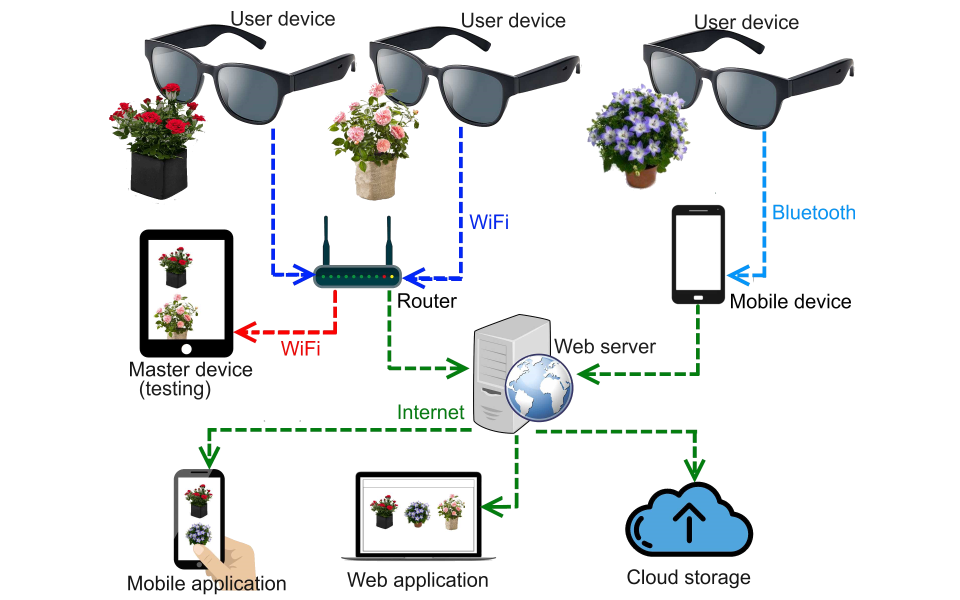
Smart glasses that take photos of the field of view using a blinking sensor and transfer the image to the cloud for further processing
 Books
Books Technology
Technology Electronics
Electronics Programming
Programming Web-interface
Web-interface Windowed Application
Windowed Application Video
Video Images
Images Audio
Audio Text
Text HTML
HTML Graphical interface
Graphical interface Lof-files
Lof-files Neural networks
Neural networks All tags
All tags Weaponry
Weaponry Arduino
Arduino Projects
Projects